What is Plant Cell Cultivation?
Unlocking the Future of Health-Promoting Ingredient Production with Plant Cell Culture
As the demand for high-quality plant bioactives continues to rise in the supplement, food, and beverage industries, businesses are increasingly looking for innovative and sustainable methods to source these valuable compounds. Plant cell culture (or plant cell cultivation) is emerging as a cutting-edge solution that offers numerous advantages over traditional agricultural practices. Plant cell cultivation is a biotech process that involves growing plant cells, tissues, or organs in controlled conditions to produce bioactive ingredients used in nutraceuticals, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food and beverage, pet foods, and beyond without the need for traditional farming. This promotes sustainable and scalable production in each industry.
Understanding Plant Cell Cultivation
Plant cell cultivation is an advanced technique that enables the production of health-promoting nutrients, known as bioactives, under highly controlled conditions, free from the variabilities associated with traditional agriculture.
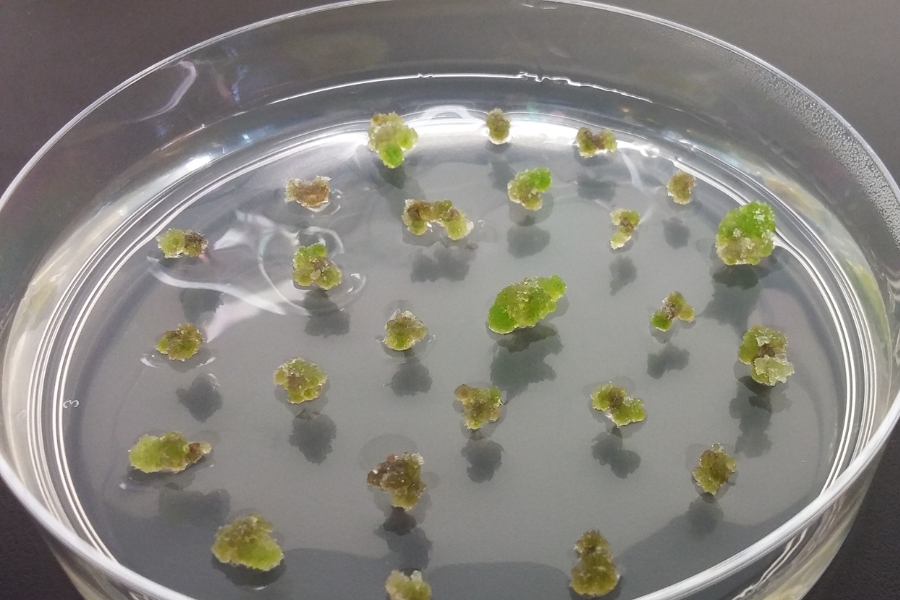
The process begins with the sampling of tissues from an authenticated plant (i.e., validated plant species) and growing them into undifferentiated cell lines. These isolated cells are then placed in a sterile, nutrient-rich medium containing vitamins, salts, sugars, and growth regulators to form a callus.
We then use state-of-the-art technologies (e.g., high throughput multi-omics) to identify the best cell line to produce certain bioactives. The cultured cells are grown in a liquid suspension and optimized for bioactives of interest.
The Technical Process of Plant Cell Cultivation
Through meticulous steps, including cell selection, optimization, and scaling, plant cell cultivation is a sustainable resource for commercial production.
- Grow: The first step in this process is to grow authenticated plants in the lab.
- Sample: Plant material is carefully selected and sterilized. Plant tissues are excised and placed in a culture medium to initiate growth.
- Generate: The culture medium is a critical component, providing all necessary nutrients and growth hormones to support cell division and de-differentiation to form a callus. The isolated cells or callus are then cultivated in a liquid suspension, controlled environment, where factors such as temperature, pH, aeration, and elicitors are meticulously adjusted to promote optimal growth and bioactive production.
- Select: State-of-the-art technologies (e.g., high throughput multi-omics) are used to identify the best cell lines to produce the bioactives of interest.
- Optimization: Once a cell line has matured through product screening, we begin process development. We grow and maintain each specific cell line in a controlled bioreactor environment to optimize cell growth and bioactive production
- Cultivation: Once the bioprocess has been developed, we scale up optimized cell lines for commercial production. Then, we harvest the cells containing the bioactives of interest. We can also extract or isolate bioactives per customer request.
Applications of Plant Cell Cultivation
Plant cell culture has and continues to have an impact in various fields, including:
- Nutraceuticals: Production of high-quality bioactives for dietary supplements.
- Functional Foods and Beverages: Incorporation of bioactives into food and drink products to enhance their health benefits.
- Pharmaceuticals: Development of plant-derived compounds for medicinal purposes.
- Cosmetics: Formulation of skincare and beauty products with potent plant bioactives.
Benefits of Plant Cell Cultivation for Businesses
Plant cell cultivation offers numerous benefits for businesses, including consistent quality, sustainability, and scalability. This innovative process ensures a reliable supply of high-quality bioactives while meeting consumer demand for safer, environmentally friendly products.
- Consistency and Quality: Plant cell culture offers unparalleled consistency in the production of bioactives. This means each batch meets the highest quality standards. Consistency is particularly important for product formulators who require reliable ingredients.
- Sustainability: By bypassing traditional farming, plant cell cultivation reduces the environmental impact associated with agriculture, such as soil depletion, pesticide use, and water consumption. This shift aligns with the growing consumer demand for sustainable products.
- Contaminant-Free: Culturing plant cells in a sterile environment eliminates the risk of contamination from heavy metals, pesticides, and other harmful substances, providing a safer, natural product for end consumers.
- Scalability: The process can be easily scaled to meet industrial demands, ensuring a steady supply of bioactives without the limitations of seasonal harvests or climatic weather events.
- Innovation and Customization: Plant cell cultivation allows for the tailored production of specific bioactives, enabling consumer packaged goods (CPG) companies to innovate and create unique formulations that stand out in the market.
Plant Cell Cultivation: Advancing Precision and Sustainability in Bioactive Production
Plant cell cultivation represents a transformative approach to sourcing bioactives, offering businesses in the supplement, food, and beverage industries a reliable, sustainable, and high-quality alternative to traditional agricultural methods. By leveraging theses advanced techniques, companies can ensure the consistent production of potent bioactives, meeting the growing demand for health-promoting ingredients while supporting environmental sustainability.
For businesses looking to stay ahead in the competitive market for bioactives, embracing plant cell cultivation is not just an opportunity—it’s a strategic imperative. Ayana Bio prides itself in its approach to plant cell cultivation. Learn more about the power of bioactives and how they can impact your business.
 BACK
BACK